Holes Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology provides a concise, accessible overview, enabling users to efficiently grasp fundamental concepts and apply them effectively.
Defining Anatomy and Physiology
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology clearly delineates these interconnected disciplines. Anatomy, derived from the Greek word meaning “to cut up,” focuses on the structure of the body and its parts – what things look like and how they are arranged. This includes both gross anatomy, visible to the naked eye, and microscopic anatomy, requiring magnification.
Conversely, Physiology explores the functions of these structures – how they work, both individually and collectively, to maintain life. It investigates the chemical and physical processes occurring within the body. Understanding both anatomy and physiology is crucial; structure dictates function, and function relies on structure.
The text emphasizes this relationship, providing a solid foundation for further study.
Levels of Structural Organization
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology systematically presents the body’s organization, beginning with the simplest level: chemicals – atoms and molecules. These combine to form cells, the basic structural and functional units of life. Similar cells are grouped into tissues, such as epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
Organs are composed of two or more tissue types working together to perform specific functions. Organ systems consist of related organs that contribute to a common purpose – like the digestive or respiratory system. Finally, the organism represents the complete living being, the sum of all structural levels.
This hierarchical arrangement demonstrates increasing complexity and integration.
The Importance of Studying A&P
Understanding Anatomy & Physiology (A&P), as presented in Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology, is crucial for numerous professions. Healthcare providers – nurses, physicians, therapists – require this knowledge for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and patient care. It’s not solely for medical fields; fitness trainers, nutritionists, and even artists benefit from understanding the human body.
A&P provides a framework for comprehending how the body functions in health and disease. It fosters informed decision-making regarding personal health and lifestyle choices.
Ultimately, studying A&P cultivates a deeper appreciation for the intricate and remarkable design of the human body.
Basic Life Processes
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology details vital processes – metabolism, responsiveness, movement, growth, reproduction, and maintaining homeostasis – for survival.
Metabolism
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explains metabolism as the sum of all chemical processes occurring within the body. This includes catabolism, the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy, and anabolism, the building of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy.
The text details how metabolic processes are crucial for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. It emphasizes the role of enzymes as catalysts in these reactions, accelerating the rate without being consumed. Furthermore, Holes clarifies the importance of energy currency, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), generated through cellular respiration, powering various bodily functions. Understanding metabolic pathways is presented as fundamental to comprehending overall physiological function.
Responsiveness
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology defines responsiveness as the ability of an organism to detect and react to changes in its internal or external environment. This crucial life process ensures survival by allowing the body to maintain homeostasis. The text details how receptors detect stimuli – like temperature, pressure, or chemicals – and transmit this information to the nervous system;
Holes explains that the nervous system then processes this information and initiates an appropriate response, often involving muscle contraction or glandular secretion. This interplay between receptors, the nervous system, and effectors is thoroughly explored. The book emphasizes that responsiveness is fundamental for adapting to changing conditions and maintaining a stable internal environment, vital for life.
Movement
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively covers movement, detailing it as a fundamental characteristic of all living organisms. The text explains that movement encompasses a wide range of activities, from the contraction of skeletal muscles resulting in locomotion, to the movement of substances across cell membranes. Holes meticulously describes the roles of the muscular and skeletal systems in producing body movements.
Furthermore, the book explores internal movements, such as the beating of the heart, the movement of food through the digestive system, and the transport of materials within the circulatory system. It emphasizes the importance of coordinated muscle contractions and nerve impulses in achieving purposeful movement. Holes clarifies how these systems work together to enable organisms to interact with their environment.
The Chemical Basis of Life
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology details how life’s chemical processes rely on atoms, molecules, and bonds, forming the basis for all bodily functions.
Atoms, Molecules, and Chemical Bonds
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously explains that all living matter is composed of atoms, the smallest units of an element. These atoms combine to form molecules, held together by chemical bonds. The text details various bond types – ionic, covalent, and hydrogen – and their roles in creating stable compounds crucial for life.
It clarifies how electron interactions dictate bond formation and strength, influencing the properties of resulting molecules. Understanding these fundamental principles is vital, as molecules like water, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are the building blocks and functional components of the human body. The book emphasizes how molecular shape directly impacts biological activity, highlighting the importance of chemical structure in physiological processes.
Major Organic Molecules (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acids)
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively covers the four major organic molecule classes vital for life. Carbohydrates provide energy and structural support, while lipids store energy, insulate, and form cell membranes. Proteins, constructed from amino acids, perform diverse functions – enzymes, hormones, structural components, and more.
Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information. The text details the monomers (building blocks) of each class, their polymerization processes, and resulting complex structures. It emphasizes the relationship between molecular structure and function, illustrating how each molecule’s unique properties contribute to specific physiological roles within the human body. Understanding these organic molecules is foundational to comprehending biological processes.
Water and its Importance
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology highlights water as the most abundant molecule in the body, crucial for maintaining life. It serves as an excellent solvent, facilitating chemical reactions and transporting substances. Water’s high heat capacity helps regulate body temperature, preventing drastic fluctuations. Its cohesive properties contribute to surface tension, essential for lung function and capillary action.
The text details water’s role in metabolic processes, lubrication of joints, and cushioning of organs. Dehydration’s detrimental effects are also emphasized, illustrating the body’s dependence on fluid balance. Understanding water’s unique chemical properties and physiological roles is fundamental to grasping overall human body function and homeostasis.
Cellular Structure and Function
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology details cells as the basic structural and functional units, exploring their components and vital processes.
The Plasma Membrane
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explains the plasma membrane as a crucial outer boundary of every cell. It’s a selectively permeable barrier, controlling what enters and exits, maintaining cellular integrity. The text details its phospholipid bilayer structure, embedding proteins for transport, enzymatic activity, and cell signaling.
It clarifies how this membrane isn’t just a passive barrier, but actively regulates passage via diffusion, osmosis, and active transport mechanisms. Holes emphasizes the importance of membrane proteins – channels, carriers, and pumps – in facilitating these processes. Understanding the plasma membrane is fundamental to grasping cellular function, as it dictates the cell’s interaction with its environment and maintains homeostasis. The book provides clear illustrations and explanations of these complex concepts.
Cytoplasm and Organelles
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously details the cytoplasm, the gel-like substance within cells, and the organelles it houses. It explains how the cytoplasm provides a medium for biochemical reactions and supports the organelles’ functions. The text thoroughly covers key organelles like the nucleus (control center), mitochondria (energy production), ribosomes (protein synthesis), and endoplasmic reticulum (transport and modification).
Holes clarifies the roles of the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes in cellular processing and waste removal. It emphasizes how each organelle contributes to the cell’s overall function and survival. Clear diagrams and concise explanations make understanding these complex structures accessible. The book stresses the interdependence of organelles, highlighting how they work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and perform specialized tasks.
Cell Transport Mechanisms
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explains how substances move across the cell membrane, crucial for cellular function. It details passive transport mechanisms – diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion – requiring no energy expenditure. The text clearly illustrates how concentration gradients drive these processes, maintaining cellular equilibrium.
Holes then elucidates active transport, demanding energy (ATP) to move substances against their concentration gradients. It covers endocytosis (bringing substances into the cell) and exocytosis (releasing substances from the cell), detailing phagocytosis and pinocytosis. The book emphasizes the importance of these mechanisms in nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cellular communication. Diagrams and examples enhance understanding of these vital processes, linking them to physiological functions.
Tissues: The Building Blocks of the Body
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously details the four tissue types – epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous – and their roles.
Epithelial Tissue
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively covers epithelial tissue, highlighting its crucial role in covering body surfaces and lining body cavities. The text details its primary functions: protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception.
It meticulously explains the classifications of epithelial tissues based on both cell shape – squamous, cuboidal, and columnar – and layering – simple and stratified. The resource clarifies how these structural differences correlate with specific functional capabilities within the body.
Furthermore, Holes elucidates specialized epithelial types like pseudostratified columnar epithelium and transitional epithelium, detailing their unique characteristics and locations. The book also emphasizes the importance of cell junctions in maintaining epithelial integrity and facilitating communication between cells, providing a solid foundation for understanding tissue function.
Connective Tissue
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology provides a detailed exploration of connective tissues, emphasizing their diverse roles in supporting, connecting, and separating different tissues and organs. The text meticulously outlines the four main classes: connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood.
It thoroughly explains the common characteristics of connective tissues, including abundant extracellular matrix composed of ground substance and fibers (collagen, elastic, and reticular). Holes clarifies how variations in these components determine the specific properties and functions of each connective tissue type.
The resource details subtypes like dense regular, dense irregular, and adipose tissue, alongside the different types of cartilage (hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage). It also covers bone structure and blood composition, offering a comprehensive understanding of these vital tissues and their contributions to overall body function.
Muscle Tissue
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology delivers a clear and concise examination of the three primary muscle tissue types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. The text meticulously details the unique structural and functional characteristics of each, emphasizing their roles in generating movement and maintaining bodily functions.
It thoroughly explains skeletal muscle’s voluntary control and striated appearance, cardiac muscle’s involuntary rhythmicity and branching fibers, and smooth muscle’s involuntary contractions in internal organs. Holes clarifies the mechanisms of muscle contraction, including the sliding filament theory and the role of calcium ions.
The resource also covers muscle fiber arrangements and their impact on force production, providing a comprehensive understanding of how muscles contribute to locomotion, posture, and vital physiological processes; It’s a valuable resource for grasping muscle physiology.
Nervous Tissue
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology provides a focused exploration of nervous tissue, the body’s rapid communication network. The text clearly delineates the two main cell types: neurons and neuroglia, detailing their distinct structures and functions. It explains how neurons transmit electrical signals via action potentials, enabling communication throughout the body.
Holes meticulously describes the components of a neuron – dendrites, cell body, and axon – and how they contribute to signal transmission. It also clarifies the roles of various neuroglial cells in supporting, protecting, and nourishing neurons. The resource covers synaptic transmission and the influence of neurotransmitters.
Furthermore, it offers a solid foundation for understanding how nervous tissue facilitates sensory perception, motor control, and higher-level cognitive functions, making it a crucial component of overall bodily regulation.

The Integumentary System
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology details the skin’s structure – epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis – and its vital protective and regulatory functions.
Structure of the Skin
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explains the skin’s layered structure. The epidermis, the outermost layer, is primarily composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, providing a protective barrier. Beneath lies the dermis, a thicker layer containing connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, and accessory structures like hair follicles and glands.
The dermis supports the epidermis and provides nourishment. Deepest is the hypodermis (subcutaneous layer), rich in adipose tissue, offering insulation and cushioning. Holes details the specific cell types within each layer – keratinocytes, melanocytes, fibroblasts, and more – and their individual roles in maintaining skin integrity and function. Understanding these structural components is crucial for comprehending the skin’s diverse physiological roles.
Functions of the Skin
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously outlines the skin’s multifaceted functions. Primarily, it acts as a protective barrier against pathogens, UV radiation, and physical trauma. The skin regulates body temperature through sweat gland activity and blood vessel dilation/constriction, maintaining homeostasis.
Furthermore, it’s a vital sensory organ, housing receptors for touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. Holes emphasizes the skin’s role in vitamin D synthesis upon sun exposure, crucial for calcium absorption. It also participates in excretion of wastes through sweat. The text details how these functions are interconnected and essential for overall health, highlighting the skin’s dynamic role beyond simple coverage.
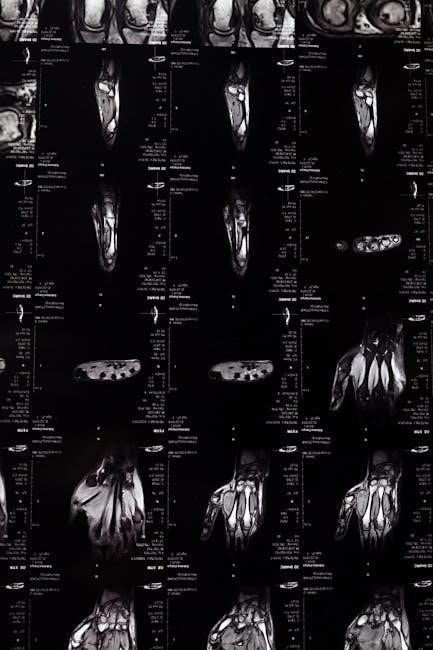
Skeletal System
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology details the skeletal system’s structure, function, and bone types, emphasizing support, protection, and movement capabilities.
Bone Structure and Types
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explores bone structure, detailing compact and spongy bone tissues, and their respective functions in providing strength and flexibility. The text elucidates the microscopic anatomy, including osteons, canaliculi, and bone cells like osteoblasts and osteoclasts, crucial for bone remodeling.
Furthermore, it classifies bone types – long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid – explaining how their shapes correlate with specific roles within the skeletal system. The book details the composition of bone matrix, highlighting organic (collagen) and inorganic (hydroxyapatite) components. It also covers periosteum and endosteum functions, vital for bone growth, repair, and nutrient supply. Understanding these structural elements and classifications is fundamental to grasping skeletal system mechanics.
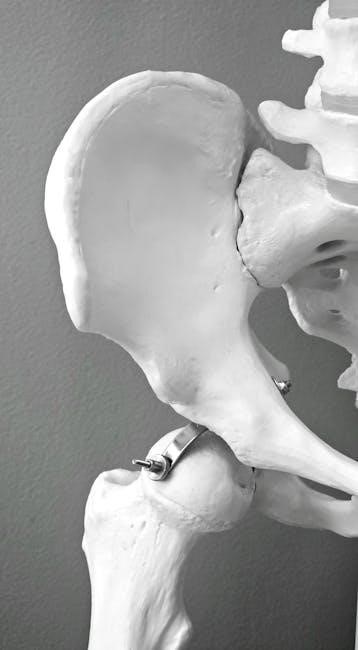
Joints
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology provides a detailed examination of joints, the points where bones articulate. The text categorizes joints structurally – fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial – explaining their unique compositions and degrees of movement. Synovial joints receive particular attention, with descriptions of their key features: articular cartilage, joint capsule, synovial fluid, and ligaments.
The book further classifies synovial joints based on movement capabilities – hinge, pivot, ball-and-socket, saddle, plane, and condyloid – illustrating each with examples. It explains how joint structure dictates range of motion and stability. Discussions include common joint injuries and disorders, emphasizing the importance of joint health for overall mobility and function. Understanding these classifications is key to appreciating skeletal system dynamics.

Muscular System
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively details muscle tissues, contraction mechanisms, and the roles of skeletal muscles in movement and posture.
Types of Muscle Tissue
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously outlines the three primary types of muscle tissue: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle, responsible for voluntary movements, is characterized by its striated appearance and attachment to bones. The text details its structure, from muscle fibers to fascicles, and explains the role of tendons in facilitating movement.
Smooth muscle, found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach and blood vessels, is involuntary and lacks striations. Holes clarifies its function in processes like peristalsis and vasoconstriction. Finally, cardiac muscle, exclusive to the heart, exhibits striations but operates involuntarily, ensuring rhythmic contractions for blood circulation. The book thoroughly explains the unique features of each muscle type, including their microscopic anatomy and physiological properties, providing a solid foundation for understanding muscular function.
Muscle Contraction
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explains the intricate process of muscle contraction, beginning with the neuromuscular junction and the release of acetylcholine. The text details the sliding filament theory, illustrating how actin and myosin filaments interact to shorten the sarcomere, ultimately causing muscle contraction.
It clarifies the roles of calcium ions, ATP, and the proteins troponin and tropomyosin in regulating this process. Holes also distinguishes between isotonic and isometric contractions, explaining how muscle tension varies during different types of activity. Furthermore, the book explores the concepts of muscle fatigue and rigor mortis, providing a complete understanding of the physiological mechanisms underlying muscle function and the factors that can influence it.
Nervous System
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously details the nervous system, covering neurons, neuroglia, brain structures, and spinal cord functions for clarity.
Neurons and Neuroglia
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively explores neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, detailing their structure – including dendrites, cell bodies, and axons – and their crucial role in transmitting electrical signals. The text elucidates the diverse types of neurons, categorized by function, such as sensory, motor, and interneurons.
Furthermore, it provides a detailed examination of neuroglia, the supportive cells of the nervous system. Holes clearly explains the various types of glial cells – astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and Schwann cells – and their specific functions in supporting, protecting, and nourishing neurons. The book emphasizes how these glial cells are vital for maintaining the nervous system’s overall health and efficient operation, going beyond simply being “support” cells.
Brain and Spinal Cord
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology delivers a thorough exploration of the central nervous system, beginning with the brain. It meticulously details the brain’s major regions – cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem – outlining their distinct structures and associated functions, including control of movement, sensation, and higher cognitive processes. The text clarifies the roles of specific brain lobes and their contributions to complex behaviors.
The book then transitions to the spinal cord, describing its anatomy and its critical role as a pathway for signals between the brain and the periphery. Holes explains the organization of spinal nerves and the mechanisms of reflex arcs. It emphasizes the protective structures surrounding both the brain and spinal cord, highlighting their importance in maintaining neurological function and preventing injury.
Endocrine System
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology comprehensively covers the endocrine system, detailing hormones, glands, and their crucial roles in bodily regulation and homeostasis.
Hormones and their Functions
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology meticulously explains hormones as chemical messengers, vital for coordinating diverse bodily functions. The text details how these substances, produced by endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream to target cells, initiating specific responses.
It clarifies the classification of hormones – including amino acid derivatives, peptides, and steroids – and their mechanisms of action. The book explores hormone effects on metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
Furthermore, Holes emphasizes the importance of feedback loops, both positive and negative, in maintaining hormonal balance (homeostasis). Detailed explanations of key hormones like insulin, thyroid hormone, and cortisol, alongside their respective functions, are provided, offering a robust understanding of endocrine regulation.
Major Endocrine Glands
Holes’ Essential of Human Anatomy & Physiology provides a comprehensive overview of the major endocrine glands and their locations within the body. The text meticulously details the pituitary gland – often called the “master gland” – and its crucial role in regulating other endocrine organs.
It further explores the thyroid and parathyroid glands, focusing on their impact on metabolism and calcium homeostasis. Detailed descriptions of the adrenal glands, pancreas, and gonads (ovaries and testes) are included, highlighting their hormone production and functions.
Holes also clarifies the anatomical relationship between these glands and their target tissues, enhancing understanding of endocrine system integration. Visual aids and clear explanations facilitate learning about each gland’s unique structure and hormonal contributions to overall body function.


